Insurance Benefit Verification for Multi-Plan and Secondary Coverage Checks
Many patients have more than one insurance plan, which means coverage details need closer review before services are provided. Insurance Benefit Verification helps confirm eligibility, identify payer responsibility, and understand how primary and secondary plans apply. When benefits are reviewed early, billing issues and follow-up questions can be reduced. This blog explains how multi-plan and secondary coverage checks support better billing and clearer insurance handling.
Table of Contents
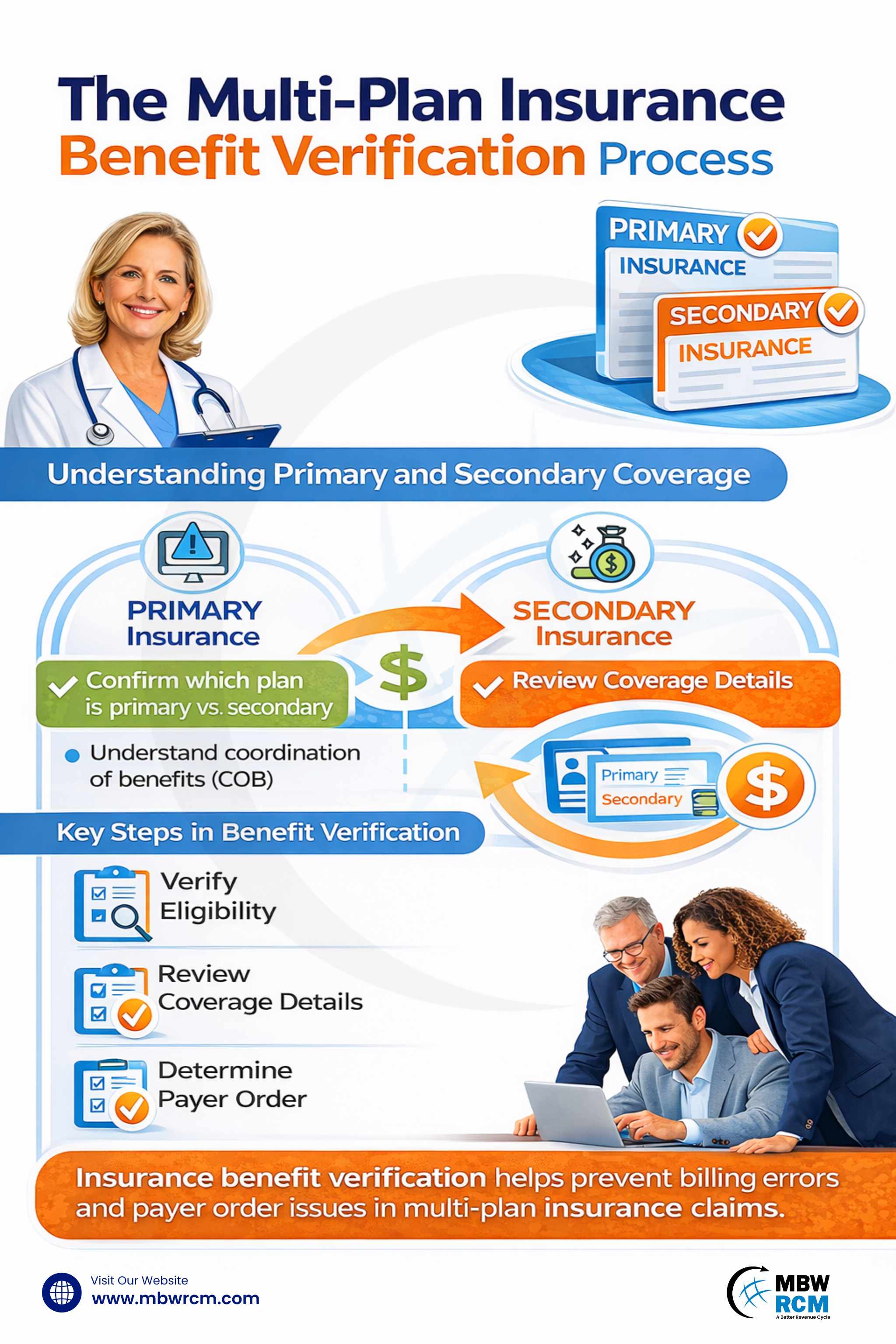
Understanding Multi-Plan and Secondary Insurance Coverage
Multi-plan insurance coverage refers to a situation where a patient has more than one active health insurance policy. This may involve employer insurance combined with another commercial policy or government-sponsored coverage. Within this structure, one plan is assigned as primary, while others act as secondary or tertiary payers.
Secondary coverage does not replace the primary plan. Instead, it responds after the primary insurer processes the claim. Multi-plan insurance verification helps confirm how these plans coexist and what portion of services may be eligible under each policy.
Importance of Benefit Verification in Multi-Insurance Coverage
Insurance Benefit Verification helps providers understand coverage limits, service eligibility, and payer responsibilities before care begins. When multiple plans exist, this review becomes more important because incorrect assumptions about coverage order can lead to billing errors.
Through Medical insurance eligibility verification, staff can confirm whether coverage is active on the date of service and whether the plan supports the scheduled treatment. This review also supports Patient Insurance Eligibility Verification, which helps patients understand their insurance position upfront.
Key Steps in Multi-Plan Benefit Verification
The Insurance benefit verification process for multi-plan coverage involves confirming active insurance, reviewingbenefit details, and identifying how primary and secondary plans apply. This review helps clarify coverage responsibility and supports correct handling of multiple insurance policies before services are delivered.
Step 1: Collect Complete Insurance Information
The process starts by collecting full insurance details from the patient. This includes policy numbers, subscriber names, relationship to the policyholder, plan type, and coverage dates for all plans listed. Accurate collection at intake supports the patient insurance verification process and prevents delays caused by missing or outdated information.
Step 2: Validate Coverage Eligibility for Each Plan
Each listed policy is checked individually to confirm active coverage on the expected service date. Medical insurance eligibility verification confirms whether the plan is active, inactive, or pending. Most payers refresh eligibility data every 24 hours, which makes verification within 1–3 days of service necessary for reliable results.
Step 3: Identify Primary and Secondary Payer Order
After eligibility is confirmed, payer responsibility is established. Primary and secondary insurance verification relies on employment status, subscriber role, and federal guidelines. Correct payer order is required to verify primary and secondary insurance and avoid claim rejection due to incorrect submission sequence.
Step 4: Review Covered Services and Benefit Limits
Each plan is reviewed to confirm covered services, visit limits, exclusions, and remaining benefits. This step supports multiple insurance plan verification by identifying overlaps or gaps between plans. Verification teams usually document benefit summaries within one business day to support billing and scheduling decisions.
Step 5: Confirm Coordination of Benefits Rules
Coordination rules determine how remaining balances are handled after the primary plan pays. Coordination of benefits (COB) verification clarifies secondary payment responsibility, allowable amounts, and coverage conditions. This step is especially important when secondary plans apply cost-sharing rules differently.
Step 6: Check Authorization and Referral Requirements
Authorization rules are reviewed separately for each plan. Some services may require approval from the primary plan, the secondary plan, or both. Identifying these requirements early helps prevent delays and supports smoother insurance verification in medical billing.
Step 7: Document Verification Results Clearly
All verification findings are recorded, including payer responses, reference numbers, coverage notes, and benefit limits. Clear documentation supports benefit verification in medical billing and helps teams respond to audits or claim inquiries. Most organizations retain verification records for 30 to 90 days.
Step 8: Reverify When Coverage or Services Change
If the service date changes or treatment plans are updated, benefits should be rechecked. Coverage status and limits can change monthly or mid-cycle. Reverification ensures that insurance benefit verification remains current and aligned with payer rules at the time of service.
Identify Primary vs Secondary Insurance Responsibility
Determining payer order within Insurance Benefit Verification identifies which insurance plan pays first and which follows. Employment status, policyholder role, and Medicare Secondary Payer rules guide this determination. Coverage responsibility is commonly reviewed 1–2 business days before the scheduled service.
Primary and secondary insurance verification supports correct claim sequencing and payment handling. For public insurance cases, Medicaid secondary insurance verification confirms eligibility and coverage limits. Most state systems update eligibility information every 24–48 hours, making timely checks necessary before billing.
Factors That Determine Primary and Secondary Insurance Responsibility:
How Primary & Secondary Insurance Plans Work Together in Verification
Insurance Benefit Verification explains how primary and secondary insurance plans function together during claim processing. Through Coordination of benefits (COB) verification, the primary plan pays first, and the secondary plan reviews the remaining balance. This coordination usually occurs within 30–60 days after the primary claim is processed.
Secondary coverage applies based on policy terms, which affects Insurance verification in medical billing and payment timing. Secondary plans may:
Cover remaining deductibles or coinsurance
Reduce patient responsibility
Deny balances not allowed under secondary policy rules
This interaction directly influences reimbursement accuracy and patient billing outcomes.
Common Challenges in Multi-Plan and Secondary Coverage Verification
Verifying benefits for multiple insurance plans involves reviewing eligibility, payer order, and coverage interaction. When primary and secondary policies apply, differences in payer rules and system updates can create verification challenges. Understanding these issues supports more effective multi-plan and secondary coverage management.
Conflicting Primary and Secondary Payer Assignments
In multi-plan cases, insurers may assign payer order differently for the same patient. These conflicts affect Benefit Verification in Medical Billing and require manual payer confirmation. Resolving payer responsibility disputes often delays claims by 15–30 days and increases rework across both primary and secondary coverage.
Delayed Coordination of Benefits Updates Between Plans
Coordination of benefits (COB) verification updates do not synchronize across insurers. When coverage changes, secondary plans may take 30–90 days to reflect updated payer order. During this period, claims may suspend or deny, affecting both multi-plan and secondary billing accuracy.
Inconsistent Eligibility Data Across Multiple Insurance Systems
Eligibility data may differ between primary and secondary insurers due to varying refresh cycles. Primary plans often update daily, while secondary plans update weekly. These inconsistencies disrupt Insurance Benefit Verification and increase verification errors near policy start or end dates.
Limited Benefit Visibility for Secondary Plans in Multi-Plan Cases
Secondary insurers frequently provide limited electronic access to benefit details. Deductibles, coinsurance, and remaining limits often require manual review, adding 20–40 minutes per case and slowing verification when multiple plans must be evaluated together.
Complex Government and Commercial Plan Combinations
Multi-plan cases involving commercial insurance with government coverage require additional checks. Medicaid secondary insurance verification involves state-specific rules, retroactive eligibility, and coverage limits, increasing complexity and extending claim resolution across multiple billing cycles. Understanding insurance verification in medical billing helps providers manage payer coordination when government and commercial plans apply together.
Common Issues Affecting Multi-Plan and Secondary Coverage Checks:
Best Practices for Effective Multi-Plan Verification
Benefit Verification improves when organizations apply consistent review standards for patients with multiple plans. Best Practices in Patient Benefits Verification include confirming coverage close to the service date, documenting payer responses, and rechecking benefits when care plans change. Many practices complete verification 48–72 hours before service to reduce eligibility discrepancies.
Effective best practices include:
Verifying coverage 48–72 hours before the scheduled service
Rechecking benefits within 24 hours after appointment or treatment changes
Recording payer reference numbers and responses on the same day of verification
Standardizing workflows across locations with updates synced every 12–24 hours
Auditing verification records every 30–60 days to maintain consistency
Following these practices helps teams maintain accurate, centralized benefit information. These practices also support Patient Intake Efficiency for Multi-Location Clinics, where consistent insurance data is critical.
Technology Support for Multi-Plan and Secondary Coverage Checks
Technology plays a growing role in modern verification workflows. Eligibility tools, payer portals, and clearinghouse integrations support faster checks and reduce manual effort. Many systems can return eligibility results within seconds and flag missing data automatically.
Automation also supports the Benefit Verification Process by tracking verification status, storing benefit summaries, and alerting teams when coverage expires. While technology improves speed, manual review is still required for complex multi-plan cases.
Optimize Your Multi-Plan Insurance Benefit Verification Process Today
Benefit Verification supports better communication, clearer billing outcomes, and fewer follow-ups when managed consistently. By combining structured review practices with technology tools help improve Insurance eligibility and benefits verification for multi-plan and secondary coverage.
A well-maintained process supports reliable claim submission and clearer patient expectations. For help managing complex coverage verification, contact us to learn how specialized support can assist your operations.
FAQs: Multi-Plan Coverage & Secondary Insurance Verification
Request for Information
Patients with multiple insurance plans require consistent review of primary and secondary coverage. Inconsistent verification can lead to payer order issues and delayed claims. Complete the form below to learn how insurance benefit verification services support multi-plan and secondary coverage checks and help maintain reliable billing workflows.