What Is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in Healthcare Billing?
Healthcare organizations manage thousands of patient encounters every month, yet reimbursement depends on how well billing processes perform behind the scenes. Understanding what is revenue cycle management in healthcare billing helps providers see how patient access, coding, claims, and payments connect into one continuous workflow.
From reducing denials to improving turnaround times, an effective revenue cycle supports operational stability, payer compliance, and predictable reimbursement across hospitals, clinics, and specialty practices.
Table of Contents
What Is Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare?
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in healthcare is the process of managing patient billing and reimbursement from appointment scheduling to final payment. It includes insurance verification, clinical documentation, medical coding, claims submission, payment posting, denial management, and patient collections. Effective RCM ensures accurate reimbursement, reduces claim denials, improves operational efficiency and supports the financial stability of healthcare providers.
Importance of Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management
Healthcare revenue cycle management supports timely reimbursement by coordinating patient access, coding, claim submission, and payment follow-up. A well-structured medical billing revenue cycle helps reduce billing errors, limit rework, and shorten accounts receivable aging.
Many organizations target claim turnaround within 30–45 days and maintain denial rates below 5% by applying consistent workflows across front-end, mid-cycle, and post-bill activities.
What Are the Steps in Healthcare Revenue Cycle?
The steps in the healthcare revenue cycle describe how patient and billing information moves from scheduling through claim processing and payment follow-up. Gaps early in the workflow can result in claim rejections, delayed reimbursement, and longer accounts receivable timelines. The following are the stages of the healthcare revenue cycle.
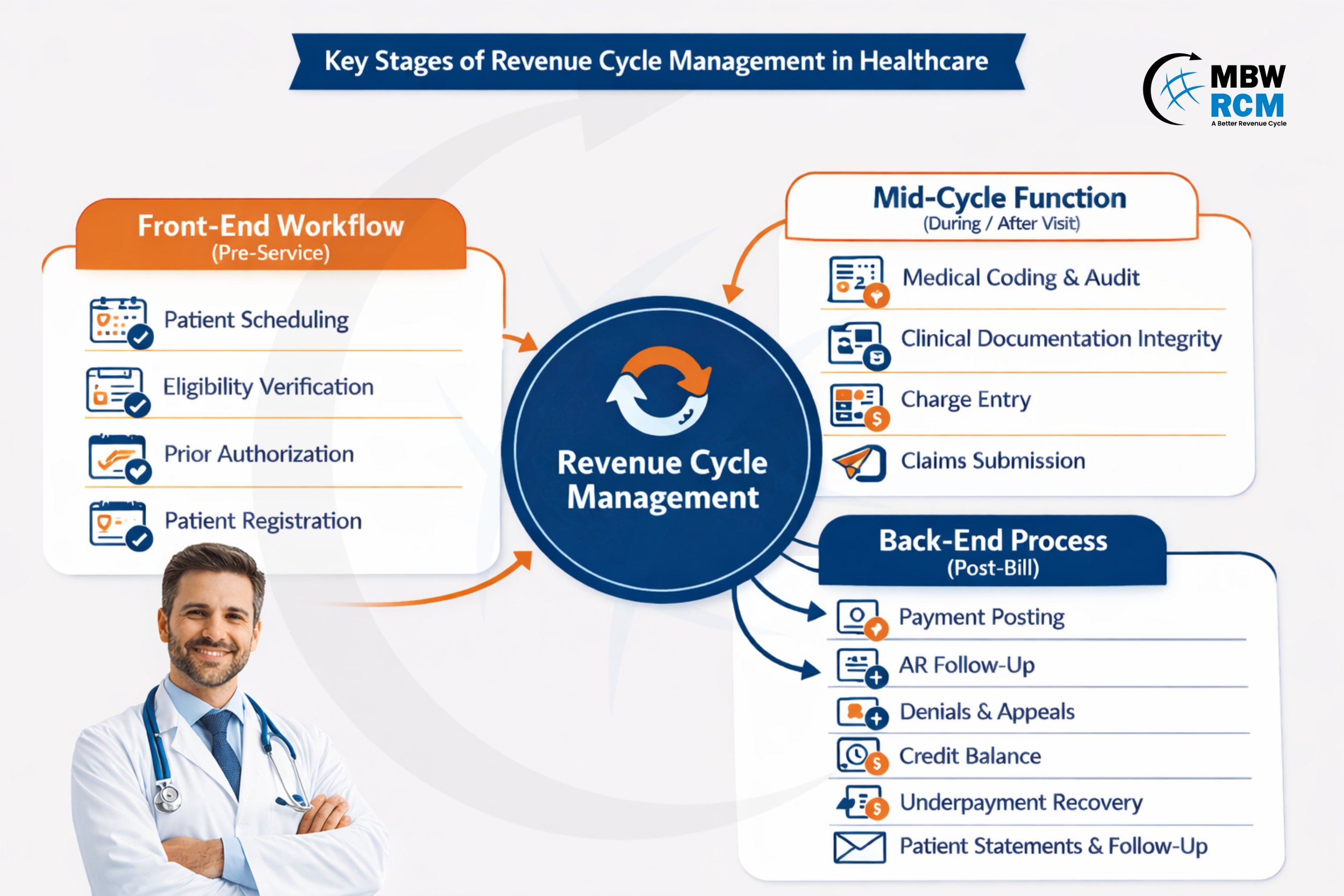
1. Front-End Workflow (Pre-Service)
The Front End Revenue Cycle establishes the administrative and coverage details required before care delivery.
Patient Scheduling: Creates the initial encounter record and links services to providers, locations, and visit types used later in billing.
Eligibility Verification: Validates active insurance, benefit limits, and patient responsibility, helping prevent eligibility-related denials.
Prior Authorization: Secures payer approval for procedures, reducing post-service claim rejections tied to coverage rules.
Patient Registration: Captures demographic and insurance data; incomplete or incorrect entries account for nearly 40% of avoidable claim errors.
2. Mid-Cycle Function (During / Right After the Visit)
This phase converts clinical activity into billable data that supports compliant claim creation.
Clinical Documentation Integrity: Ensures provider notes support medical necessity and billed services.
Medical Coding & Audit: Assigns ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes while reviewing compliance and payer guidelines.
Charge Entry: Records all billable services, where missed charges can lead to 3–6% revenue leakage.
Claims Submission: Formats and transmits claims to payers, often through clearinghouses that perform initial edits and validations.
This stage is frequently supported by revenue cycle management solutions designed to reduce manual errors and rework.
3. Back-End Process (Post-Bill)
After claim submission, reimbursement tracking and resolution activities begin.
Payment Posting: Applies payer remittances, contractual adjustments, and patient responsibility amounts.
AR Follow-up: Prioritizes unpaid claims, commonly segmented into 30-, 60-, and 90-day aging buckets.
Denials and Appeals: Addresses rejected claims, with many organizations targeting appeal resolution within 14–30 days.
Credit Balance: Reviews prevent unresolved overpayments from remaining on patient accounts.
Underpayment Recovery: Identifies reimbursement shortfalls based on contracted payer rates.
Patient Statements and Follow-up: Manage remaining balances, payment plans, and patient communication.
Many organizations rely on healthcare RCM services to manage this stage efficiently and maintain consistent follow-up.
Revenue Cycle vs Medical Billing: What’s the Difference?
Revenue cycle management compared to medical billing differs in scope and responsibility. Medical billing handles coding, claim submission, and payment posting after services are delivered, typically within 7–14 days of a patient visit.
The revenue cycle spans pre-visit tasks such as eligibility checks and continues through denial resolution and patient follow-up, which can extend 30–90 days. Many providers use medical billing and RCM services to align workflows, reduce rework, and maintain consistent reimbursement timelines.
Revenue Cycle vs Medical Billing Comparison
Common Challenges in Healthcare Revenue Cycle
Healthcare organizations face several operational challenges across the revenue cycle that affect claim processing and payment timelines. When not addressed early, these issues can increase denials, extend accounts receivable aging, and add rework for billing teams and providers.
Payer Policy Changes and Coverage Updates
Frequent payer policy updates affect coverage rules, modifiers, and documentation requirements. Missed changes often lead to claim rejections or delayed adjudication, increasing rework and extending reimbursement timelines by 15–30 days for hospitals and physician billing teams.
Authorization and Eligibility Verification Gaps
Missing or incomplete eligibility checks and prior authorizations remain a major source of preventable denials. These gaps commonly delay payments by 20–45 days, requiring resubmission and additional administrative effort to recover reimbursement. To learn more about effective revenue cycle steps, refer to this guide.
Documentation and Coding Alignment Issues
When clinical documentation does not fully support ICD-10 or CPT codes, claims may be downcoded or denied. Internal audits frequently identify documentation-related errors in 5–10% of submitted claims, increasing compliance risk and rework.
Specialty-Specific Billing and Payer Variability
Specialty services face higher denial exposure due to procedure-level rules and payer scrutiny. These RCM challenges in specialty healthcare are common in cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, and behavioral health, where coverage criteria vary widely across payers.
Staffing Constraints and Manual Follow-Up Processes
Limited billing staff and manual workflows can cause unpaid claims to age beyond 60–90 days, increasing the risk of missed appeal deadlines and reduced reimbursement recovery.
Benefits of Revenue Cycle Management Healthcare
Revenue cycle management delivers value through improved claim turnaround, fewer denials, and clearer financial visibility. Organizations using structured workflows supported by outsourced revenue cycle management often experience shorter payment cycles and improved control over accounts receivable.
Key benefits include:
➤ Faster claim turnaround, often within 30–40 days
➤ Reduced denial rates, typically below 5%
➤ Better visibility into 30-, 60-, and 90-day A/R aging
➤ Improved efficiency without increasing internal overhead
Revenue Cycle Metrics to Track in Healthcare Billing
Revenue cycle performance depends on measurable indicators that show how efficiently claims move from submission to payment. Monitoring metrics helps identify payer delays, workflow gaps, and follow-up priorities. Many organizations compare results against a Revenue Cycle Benchmark to evaluate performance across payers and service lines.
Key metrics to track include:
Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R): Target under 40 days
Clean Claim Rate: Above 95%
Denial Rate: Below 5%
A/R Aging: Balances tracked in 30-, 60-, and 90-day buckets
First-Pass Resolution Rate: Claims paid on first submission, target 90–95%
Net Collection Rate: Reimbursement collected vs expected, target 95%+
Revenue Cycle Technology in Healthcare
Revenue cycle technology supports billing, claims, and payment workflows by integrating EHRs, practice management systems, and payer portals. These platforms automate data exchange and reduce manual effort across the billing lifecycle.
In healthcare organizations, revenue cycle technology supports:
Front-end RCM - Eligibility and authorization tracking
Mid-cycle - Coding validation and charge capture
Back-end workflows - Claims, payments, and denial monitoring
Using Healthcare Revenue Cycle Analytics, organizations can identify payer trends and underpayment issues within 7–14 days, improving follow-up efficiency and reimbursement outcomes.
Future Trends in Healthcare Revenue Cycle
Healthcare revenue cycle operations are moving toward greater automation and predictive decision-making. Key future trends in revenue cycle management include expanded use of AI for denial prevention, real-time eligibility and authorization checks at scheduling, and payer-specific rule engines embedded in billing systems.
Over the next 3–5 years, organizations are expected to adopt proactive, data-driven workflows that identify issues before claim submission, reducing manual follow-up and reimbursement delays.
Conclusion
Effective billing performance depends on how well each stage of the healthcare revenue cycle is managed, from patient access to final payment resolution. Understanding what is revenue cycle management helps organizations reduce delays, limit denials, and improve reimbursement consistency. If you are evaluating revenue cycle management services to strengthen billing operations and financial outcomes, contact MBW RCM to discuss solutions that align with your organization’s needs.
FAQs: Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Request for Information
Fill out the form to understand how revenue cycle management supports healthcare billing and reimbursement. Our specialists review revenue cycle workflows to identify gaps that may affect claim processing and payment timelines.
Gain clarity on your current revenue cycle approach and take informed steps to improve billing performance.