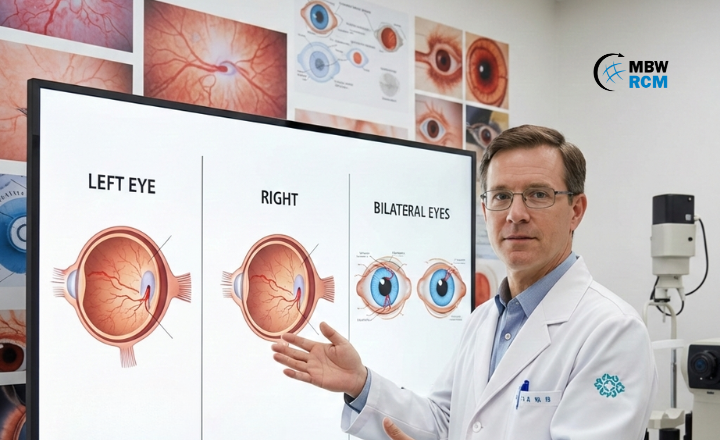
Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code for Left, Right & Bilateral Eyes
Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code is used to classify retinal detachment conditions for clinical documentation, medical reporting, and insurance claim processing. Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition where the retina separates from underlying tissue and may lead to vision loss if untreated. ICD-10 category H33 includes multiple classifications based on detachment type and eye laterality, including right eye, left eye, and bilateral involvement.
This blog explains retinal detachment ICD-10 codes for left eye, right eye, and bilateral eye conditions, along with commonly used diagnosis codes and documentation requirements.
Understanding Retinal Detachment in ICD-10
Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Codes are diagnosis codes used to classify and report retinal detachment conditions in medical records under the ICD-10 system. These codes mainly fall under category H33, which covers retinal detachments and retinal breaks.
The ICD-10 classification system helps identify the type of detachment, such as detachment with retinal break, serous retinal detachment, or traction retinal detachment.
These codes are used for clinical documentation, treatment planning, insurance claims, and disease tracking. It also supports laterality reporting, which indicate whether the condition affects the right eye, left eye, or both eyes.
Why Laterality is Important in Retinal Detachment Coding
Laterality identifies which eye is affected and is required for eye laterality coding ICD 10 compliance. Most retinal detachment codes use sixth character extensions to specify right eye, left eye, or bilateral eye involvement. In ICD-10-CM, laterality is built into many ophthalmology codes to improve coding specificity and claim reliability.
ICD-10 Laterality Structure:
Right Eye → ends in 1
Left Eye → ends in 2
Bilateral → ends in 3
Unspecified → ends in 9
Correct laterality supports claim approval and improves clinical data quality. Coding teams must follow retina diagnosis documentation coding standards. Many coders use an ICD 10 eye coding cheat sheet to verify extensions. If documentation supports laterality, unspecified codes should be avoided.
Diagnosis Codes for Right Eye Retinal Detachment
Right eye detachment coding requires proper selection of break type and detachment classification. In daily practice, right eye diagnosis ICD 10 coding must match provider documentation and imaging findings.
Right Eye Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code List
Right eye retinal break with detachment codes are used when a retinal tear or break causes retinal separation in the right eye. These codes fall under the H33.0 category and require documentation of break type and detachment severity. The following list includes commonly used ICD-10 codes for right eye retinal break with detachment conditions.
H33.001 – Unspecified retinal detachment with break, right eye
H33.011 – Retinal detachment with single retinal break, right eye
H33.021 – Retinal detachment with multiple retinal breaks, right eye
H33.031 – Retinal detachment with giant retinal tear, right eye
H33.041 – Retinal detachment with retinal dialysis, right eye
H33.051 – Total retinal detachment with retinal break, right eye
When to Use
Use right eye codes when provider documentation clearly states right eye involvement. Coding should match OCT scan reports, fundus exam findings, or operative notes.
Documentation Required
Clinical documentation is required to support right eye code selection. Providers must document retinal findings, imaging, and treatment details.
Laterality confirmation
Break type description
Detachment extent
Surgical intervention details
Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code selection must always follow clinical documentation and diagnostic imaging confirmation.
Diagnosis Codes for Left Eye Retinal Detachment
Left eye coding follows the same structure but uses left eye extensions. Correct left eye diagnosis ICD 10 coding depends on tear pattern and detachment cause.
Left Eye Retinal Break With Detachment Code List
Left eye retinal break with detachment codes are used when a retinal tear or break causes retinal separation in the left eye. These codes fall under the H33.0 category and require documentation of break type and detachment severity. The following list includes commonly used ICD-10 codes for left eye retinal break with detachment conditions.
H33.002 – Unspecified retinal detachment with break, left eye
H33.012 – Retinal detachment with single retinal break, left eye
H33.022 – Retinal detachment with multiple retinal breaks, left eye
H33.032 – Retinal detachment with giant retinal tear, left eye
H33.042 – Retinal detachment with retinal dialysis, left eye
H33.052 – Total retinal detachment with retinal break, left eye
When to Use
Use left eye codes when clinical documentation confirms retinal separation only in left eye.
Documentation Required
Clinical documentation is required to support correct code selection and medical necessity. Providers must document retinal findings, imaging confirmation, and treatment details. The following clinical details help support left eye retinal detachment coding.
Fundoscopy findings
Retinal tear location
Fluid accumulation pattern
Surgical plan or observation notes
Proper Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code use helps maintain clean claim submission and supports treatment justification.
Bilateral Retinal Detachment Diagnosis Coding
Bilateral detachment requires precise bilateral eye disease coding ICD 10 selection because both eyes must be clinically confirmed as affected.
ICD-10 Codes for Bilateral Retinal Detachment Disorders
H33.003 – Unspecified retinal detachment with break, bilateral
H33.013 – Retinal detachment with single retinal break, bilateral
H33.023 – Retinal detachment with multiple retinal breaks, bilateral
H33.033 – Retinal detachment with giant retinal tear, bilateral
H33.043 – Retinal detachment with retinal dialysis, bilateral
H33.053 – Total retinal detachment with retinal break, bilateral
If documentation does not specify eye involvement, coders may temporarily use unspecified eye retinal detachment code until clarification is obtained.
When to Use
Use bilateral codes when imaging or physician documentation confirms both eyes are affected simultaneously.
Bilateral Eye Documentation and Reporting Rules
Confirmation of both eye involvement
Imaging evidence
Surgical or treatment plan for both eyes
Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code accuracy is critical when billing complex bilateral surgical procedures. Want to know the Top 10 tips for retina ICD-10 coding and documentation best practices?
Retinal Detachment Types and Their ICD-10 Code Classification
Retinal detachment is classified into different types based on how the retina separates and how subretinal fluid or fluid accumulation collects under the retinal layer. Each type is grouped under specific ICD-10 H33 subcategories. Understanding these detachment mechanisms helps in selecting the correct Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code and supports clinical reporting, surgical planning, and medical claim processing.
Retinal Detachment Classification and ICD-10 Code Mapping:
These classifications support selecting the correct Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code based on pathology mechanism, imaging findings, and clinical documentation.
How to Choose the Correct Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code
Choosing the correct Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code requires review of clinical diagnosis, imaging confirmation, and provider documentation. The following steps outline how to select the correct code based on documented findings.
Step 1: Confirm Retinal Detachment Diagnosis
Confirm retinal detachment through fundus exam, OCT imaging, or B-scan ultrasound. Providers must document detachment presence, location, and severity. This confirms the case qualifies under retinal detachment ICD classification before selecting subcategory codes.
Step 2: Identify Retinal Detachment Type
Identify if rhegmatogenous, traction, or serous detachment. Rhegmatogenous detachment (H33.0 series) occurs due to retinal tear. Traction detachment (H33.4 series) occurs due to scar tissue pulling retina. Serous detachment (H33.2 series) occurs due to subretinal fluid accumulation without tear.
Step 3: Verify Eye Laterality
Confirm right eye, left eye, or bilateral involvement using documentation and imaging. ICD-10 ophthalmology codes use laterality extensions where right eye ends in 1, left eye ends in 2, and bilateral ends in 3.
Step 4: Document Retinal Break Pattern
Document single break, multiple breaks, or giant retinal tear. Giant retinal tear usually extends more than 90 degrees of retinal circumference. Break pattern determines correct H33 subcategory code selection.
Step 5: Review Documentation for Billing and Reporting
These steps are critical in ophthalmology revenue cycle management. Many Ophthalmology Billing Companies in USA specialize in retina coding. Common Eye care Billing Challenges include incomplete documentation, unspecified laterality, and missing detachment type details.
Final selection of Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code should match physician documentation, imaging findings, and surgical reports.
Conclusion
Retinal detachment coding requires detailed clinical documentation, correct laterality selection, and precise ICD-10 mapping. Understanding detachment types and laterality extensions helps reduce coding errors and supports correct reimbursement. Using the correct Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code helps improve documentation clarity, claim approval rates, and patient data tracking across ophthalmology care systems.
For reliable ophthalmology billing services and coding support, partner with experts who understand retinal coding requirements. Contact us today to streamline billing workflows, reduce denials, and improve claim turnaround time.
FAQs: Retinal Detachment ICD-10 Coding
What does H33 mean in ICD-10 coding?
+
H33 is the ICD-10 category used for retinal detachments and retinal breaks.
How do you code retinal detachment with retinal tear?
+
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is typically coded under the H33.0 series.
When should unspecified retinal detachment code be used?
+
Unspecified retinal detachment codes should only be used when documentation does not confirm laterality or detachment type.
How is retinal detachment diagnosed clinically?
+
Retinal detachment is diagnosed using clinical fundus examination, OCT imaging, or B-scan ultrasound when visualization is limited.
Can diabetes cause retinal detachment?
+
Yes. Diabetes can lead to tractional retinal detachment due to scar tissue formation and traction on the retina.
Request for Information
Facing ophthalmology coding challenges like Retinal Detachment ICD 10 Code selection errors, laterality issues, documentation gaps, or claim denials? A coding expert can review workflows and identify improvement areas.
Fill out the form below to connect with an RCM specialist to discuss retinal ICD-10 coding challenges and improve your ophthalmology billing performance.