Best Practices for Efficient Patient Registration and Communication in the Healthcare Revenue Cycle
The financial health of a healthcare organization doesn’t begin when a claim is submitted — it starts at the front desk, during patient registration and initial communication. While these may look like routine administrative tasks, they form the structural foundation of the revenue cycle. Done right, they drive faster reimbursements, reduce denials, and create a positive patient experience. Done poorly, they generate a chain reaction of errors, delays, and lost revenue.
With patients now responsible for a higher portion of their medical bills and insurance rules evolving constantly, accuracy, efficiency, and patient engagement at the point of entry have become strategic imperatives.
Table of Contents
1. Why Patient Registration Is the Revenue Cycle’s Point of Origin
The healthcare revenue cycle is a multi-stage process that begins long before a provider sees a patient. It starts with appointment scheduling, registration, and pre-authorization — steps that determine the accuracy of everything that follows.
Why this stage matters:
Error propagation: Any mistake made here — from a misspelled name to outdated insurance details — will affect eligibility checks, claim submission, and payment collection.
Claim rejections: Payers compare the submitted data against their records. Even a minor discrepancy can trigger an automatic rejection.
Operational ripple effect: Fixing a denied claim requires additional staff time, pulls resources from current work, and delays revenue.
Example:
If a patient’s policy number is entered incorrectly, the claim may be denied within 24–48 hours. The denial triggers a rework process that can take weeks — lengthening Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R) and delaying the cash flow needed for payroll, supply purchases, or capital investment.
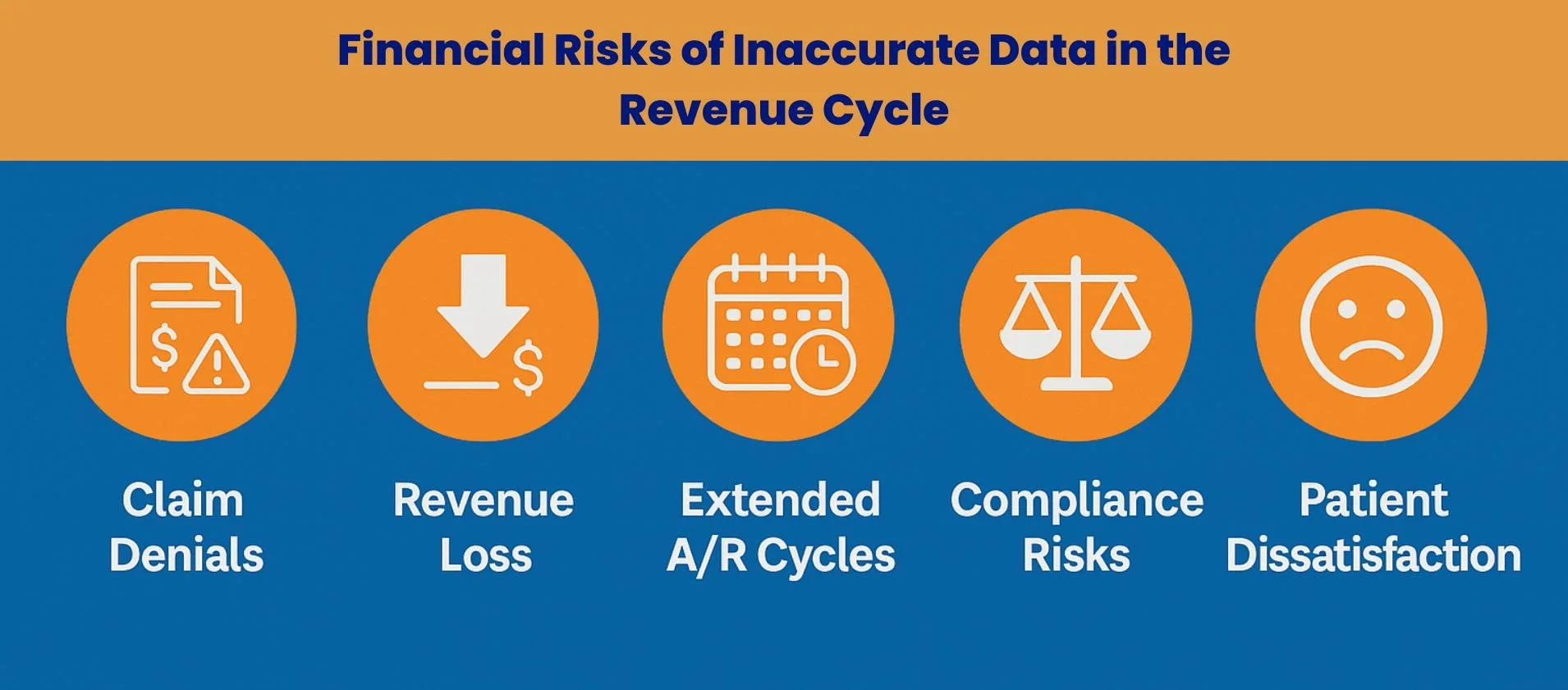
2. The Real Cost of Inaccurate Data
Next, we explore the tangible financial, operational, and reputational impacts of poor data capture at the front end, showing why every inaccurate entry at registration can cascade into costly downstream consequences.
2.1 Claim Denials and Rejections
Scope of the problem: Industry research shows that up to 35% of all claim denials stem from registration and eligibility errors.
Common causes: Typos, outdated coverage, incomplete demographic data, or failure to check pre-authorization requirements.
Impact: Denials increase operational costs and create payment delays that directly threaten financial stability.
To address these challenges, healthcare providers can follow proven tips to prevent patient registration errors that strengthen reliability and improve revenue cycle outcomes.
2.2 Administrative Rework
Each denied claim can cost $25–$118 in rework expenses, depending on complexity.
Staff must investigate the error, contact patients, update records, and resubmit claims — often with strict payer timelines.
This opportunity cost means fewer resources for new claims and patient engagement.
2.3 Patient Trust and Loyalty
Patients often experience the results of registration errors as unexpected bills.
Confusion about balances erodes trust and makes patients more likely to seek care elsewhere.
In an age where patients shop for providers like other services, billing accuracy and clarity are vital to retention.
3. Common Registration Errors and How to Avoid Them
Let us now break down the most frequent mistakes made at the point of patient registration, explain their direct impact on revenue cycle performance, and outline practical, technology-driven strategies to prevent them from occurring in the first place. To see how front-end accuracy drives financial results, read more about the crucial role of patient registration in boosting revenue and reducing claim denials.
| Error | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect insurance info | Mismatched data triggers immediate claim denial. | Real-time eligibility verification before service. |
| Incomplete forms | Delays, repeated patient contact, and rework. | Use standardized forms with required field validation. |
| Failure to update demographics | Slower collections due to outdated contact info. | Conduct regular audits; prompt patients to confirm at every visit. |
| Missing prior authorization | Nonpayment for services requiring pre-approval. | Confirm requirements before scheduling or service. |
4. Best Practices for Accurate, Efficient Registration
4.1 Follow NAHAM Standards
Core data collection: Go beyond basics — capture full legal name, DOB, address, phone, insurance details, and secondary contacts. This ensures a single source of truth across all systems.
Verification process: Always request a government-issued photo ID and insurance card at every visit, even for long-time patients, to catch changes in coverage or demographics.
Consistency in unknown data: Use agreed placeholders (e.g., 111-111-1111 for phone) to avoid mismatches in the EHR and to support data integrity audits.
Why it matters: Following NAHAM standards reduces registration error rates to industry best-practice levels (1–2%) and strengthens downstream claim acceptance.
To learn more, check out this detailed guide on the patient registration process.
4.2 Go Proactive with Pre-Service Information Gathering
Online pre-registration: Enable patients to complete intake forms, upload ID and insurance, and sign consents before arrival via secure portals or mobile apps. This also allows staff to review and correct issues before day-of service.
Insurance verification: Confirm coverage, benefits, deductibles, and patient financial responsibility ahead of the appointment to avoid day-of surprises.
Operational benefit: Reduces lobby congestion, enables pre-authorization, improves patient satisfaction, and allows scheduling to flow more predictably.
Example: Clinics that implemented pre-service checks saw up to a 20% drop in denials linked to eligibility errors.
4.3 Invest in Staff Training & Quality Assurance
Training: Hold quarterly sessions on payer policy changes, documentation protocols, and communication scripts, using real denial cases as learning tools.
Auditing: Conduct random monthly audits of registration data to catch recurring errors and provide instant feedback.
Culture of accuracy: Recognize and reward teams that maintain low error rates and high first-pass claim acceptance to reinforce desired behaviors.
Long-term impact: A trained and quality-focused team not only reduces errors but also enhances patient perception of professionalism at the first point of contact.
5. Patient Communication as a Revenue Driver
Patient communication is more than a customer service task — it is a strategic lever for accelerating revenue and improving patient satisfaction. Every interaction, from pre-visit estimates to post-care reminders, shapes a patient’s willingness and ability to meet their financial obligations. In a competitive healthcare environment where patients behave like informed consumers, practices that prioritize clear, proactive, and empathetic communication at each touchpoint often see measurable gains in both collection rates and loyalty.
Price Transparency
Federal rules (CMS Transparency in Coverage, Hospital Price Transparency) require disclosure of prices for common services.
Transparent pricing can differentiate your practice, helping patients plan and improving point-of-service collections.
Financial Literacy
Replace jargon with plain language.
Offer easy-to-read statements, FAQs, and one-on-one counseling for complex bills.
Educated patients are more likely to pay on time and in full.
Communication Touchpoints
Before care: Provide estimates and pre-registration links.
During care: Confirm financial responsibility verbally and in writing.
After care: Use text, email, and portal reminders to follow up on balances.
6. Technology That Transforms the Front End
Technology is no longer a support function at the front desk — it is a strategic enabler that can fundamentally reshape how the patient experience and revenue cycle intersect. Modern tools streamline intake, reduce human error, and provide real-time insights that were impossible a decade ago. From patient portals to AI-driven analytics, these solutions don’t just make tasks faster — they make them smarter, embedding accuracy and compliance into every step of registration and initial financial communication.
| Tool | Function | RCM Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Patient portals & digital intake | Patients self-register, upload docs, sign consents online. | Improves accuracy, reduces errors, streamlines workflows. |
| Real-time eligibility verification | Confirms coverage instantly before service. | Prevents denials, ensures correct patient responsibility collection. |
| Digital payment solutions | Offers online, mobile, and text-to-pay options. | Increases collection rates, reduces A/R days. |
| AI & automation | Automates routine tasks, analyzes denial trends. | Cuts admin burden, provides predictive insights. |
7. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Registration Error Rate (Target: 1–2%)
Why it matters: Predicts denial rates and highlights training needs.Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R) (Target: <30 days)
Why it matters: Shorter cycles improve cash flow and financial stability.Patient Responsibility Collection Rate (Target: 90%+)
Why it matters: Reflects patient engagement, communication quality, and payment option accessibility.
8. An Integrated, Sustainable Approach
For lasting improvement, combine people, process, and technology:
People: Skilled, well-trained, and empowered front-end teams.
Process: Standardized, error-proof workflows.
Technology: Automated tools for data validation, eligibility checks, and patient self-service.
Phased implementation roadmap:
Assess current registration, communication, and collection workflows.
Start improvements with patient registration accuracy.
Layer in communication enhancements, transparency, and payment tools.
Monitor KPIs, adjust processes, and expand to other RCM areas.
Conclusion
Patient registration is not a formality — it is the financial gateway of healthcare. When organizations invest in accuracy, proactive communication, and technology, they not only reduce denials and speed up payments but also improve patient trust and satisfaction.
In the revenue cycle, the front end determines the fate of the back end. Master it, and you control your financial destiny. Contact MBW RCM today and let our experts transform your front-end processes into a powerful driver of efficiency, Reliability, and revenue growth.